《「古代日本にイスラエル人がやって来た」英語ウェブサイトへの反響
じつは筆者は、20年以上前から、「古代日本にイスラエル人がやって来た」(Israelites Came to Ancient Japan)という英語版ウェブサイトを立ち上げ、その根拠をいろいろ解説してきた。
日本神道と古代イスラエル宗教の風習、祭、神殿の類似や、日本古来の伝統文化とユダヤ伝統文化の類似、遺伝子DNAの近縁・同祖性などである。
そのサイトを見て世界中の多くの方々が、反響のEメールを下さった。中にはユダヤ人のものも多く含まれていた。
彼らがいったいどのような感想を持ってくれたか、最後にここに、とくにユダヤ人からのメールを、いくつかご紹介したいと思う。それによって、一般のユダヤ人がどのような目でこの説を見ているかを、知ることができると思う。》
もう隠しきれない…より
Israelites Came to Ancient Japan

Ark of the covenant of
I am a Japanese Christian writer living in
The following sections are concerned with those Japanese traditions which possibly originated from the ancient Israelites.
The reason why I exhibit these on the internet is to enable anyone interested in this subject, especially Jewish friends to become more interested, research it for yourself, and share your findings.
 The ancient
The ancient
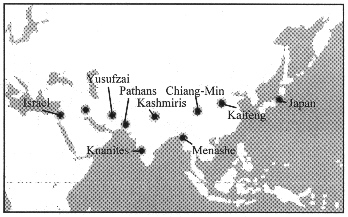
Yusufzai
They live in
Pathans
They live in
Kashmiri people
In Kashmir they have the same land names as were in the ancient northern kingdom of
Knanites
In
Shinlung tribe (Bnei Menashe)
In Myanmar (Burma) and India live Shinlung tribe, also called Menashe tribe. Menashe is Manasseh, and the Menashe tribe is said to be the descendants from the tribe of Manasseh, one of the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel. They have ancient Israeli customs.
Chiang (Qiang or Chiang-Min) tribe
They live in China and have ancient Israeli customs. They believe in one God and have oral tradition that they came from far west. They say that their ancestor had 12 sons. They have customs of Passover, purification, levirate marriage, etc. as ancient Israelites.
It is known that there had been a large Jewish community since the time of B.C.E..
I am going to discuss this on this website.

The "Suwa-Taisha" shrine
In
At Suwa-Taisha, the traditional festival called "Ontohsai" is held on April 15 every year (When the Japanese used the lunar calendar it was March-April). This festival illustrates the story of Isaac in chapter 22 of Genesis in the Bible - when Abraham was about to sacrifice his own son, Isaac. The "Ontohsai" festival, held since ancient days, is judged to be the most important festival of "Suwa-Taisha."
 At the back of the shrine "Suwa-Taisha," there is a mountain called
At the back of the shrine "Suwa-Taisha," there is a mountain called
At the festival, a boy is tied up by a rope to a wooden pillar, and placed on a bamboo carpet. A Shinto priest comes to him preparing a knife, and he cuts a part of the top of the wooden pillar, but then a messenger (another priest) comes there, and the boy is released. This is reminiscent of the Biblical story in which Isaac was released after an angel came to Abraham.
At this festival, animal sacrifices are also offered. 75 deer are sacrificed, but among them it is believed that there is a deer with its ear split. The deer is considered to be the one God prepared. It could have had some connection with the ram that God prepared and was sacrificed after Isaac was released. Since the ram was caught in the thicket by the horns, the ear might have been split.
The knife and sword used in the "Ontohsai" festival
In ancient time of

A deer with its ears split
People call this festival "the festival for Misakuchi-god". "Misakuchi" might be "mi-isaku-chi." "Mi" means "great," "isaku" is most likely Isaac (the Hebrew word "Yitzhak"), and "chi" is something for the end of the word. It seems that the people of Suwa made Isaac a god, probably by the influence of idol worshipers.
Today, this custom of the boy about to be sacrificed and then released, is no longer practiced, but we can still see the custom of the wooden pillar called "oniye-bashira," which means, "sacrifice-pillar."

The "oniye-bashira" on which the boy is supposed to be tied up
Currently, people use stuffed animals instead of performing a real animal sacrifice. Tying a boy along with animal sacrifice was regarded as savage by people of the Meiji-era (about 100 years ago), and those customs were discontinued. However, the festival itself still remains.
The custom of the boy had been maintained until the beginning of Meiji era. Masumi Sugae, who was a Japanese scholar and a travel writer in the
The festival of "Ontohsai" has been maintained by the Moriya family ever since ancient times. The Moriya family thinks of "Moriya-no-kami" (god of Moriya) as their ancestor's god. They also consider "
The Moriya family has been hosting the festival for 78 generations. And the curator of the museum said to me that the faith in the god of Moriya had existed among the people since the time of B.C.E..
Apparently, no other country but
Youtube: Suwa-taisha shrine (See after 8:00) and the second half (For English subtitles, click "Subtitles" (captions) at the right bottom of the YouTube screen)
Youtube: Ontohsai festival and interview with Arimasa Kubo
The Crest of the Imperial House of Japan Is the Same As That Found On the Gate of Jerusalem.
The crest of the Imperial House of Japan is a round mark in the shape of a flower with 16 petals. The current shape appears as a chrysanthemum (mum), but scholars say that in ancient times, it appeared similar to a sunflower. The sunflower appearance is the same as the mark at Herod's gate in


The mark on Herod's gate at
Japanese Religious Priests "Yamabushi" Put A Black Box on their Foreheads Just As Jews Put A Phylactery on their Foreheads.
"Yamabushi" is a religious man in training unique to
On the forehead of "Yamabushi," he puts a black small box called a "tokin", which is tied to his head with a black cord. He greatly resembles a Jew putting on a phylactery (black box) on his forehead with a black cord. The size of this black box "tokin" is almost the same as the Jewish phylactery, but its shape is round and flower-like.


A "yamabushi" with a "tokin" blowing a horn
Originally the Jewish phylactery placed on the forehead seems to have come from the forehead "plate" put on the high priest Aaron with a cord (Exodus 28:36-38). It was about 4 centimeters (1.6 inches) in size according to folklore, and some scholars maintain that it was flower-shaped. If so, it was very similar to the shape of the Japanese "tokin" worn by the "yamabushi".

A Jew with a phylactery blowing a shofar
Furthermore, the "yamabushi" use a big seashell as a horn. This is very similar to Jews blowing a shofar or ram's horn. The way it is blown and the sounds of the "yamabushi's" horn are very similar to those of a shofar. Because there are no sheep in
"Yamabushi" are people who regard mountains as their holy places for religious training. The Israelites also regarded mountains as their holy places. The Ten Commandments of the Torah were given on
In
There is no knowledge that a real scroll of a Jewish Torah was ever found in a Japanese historical site. However, it appears this "scroll of the tora" is a derivation of the Jewish Torah.
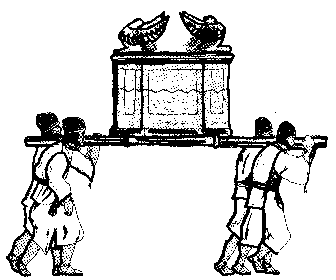
Japanese "Omikoshi" Resembles the Ark of the Covenant.
In the Bible, in First Chronicles, chapter 15, it is written that David brought up the ark of the covenant of the Lord into
"David and the elders of

Illustration of Israeli people carrying the Ark of the Covenant
When I read these passages, I think; "How well does this look like the scene of Japanese people carrying our 'omikoshi' during festivals? The shape of the Japanese 'Omikoshi' appears similar to the ark of the covenant. Japanese sing and dance in front of it with shouts, and to the sounds of musical instruments. These are quite similar to the customs of ancient

Japanese "Omikoshi" ark
Japanese carry the "omikoshi" on their shoulders with poles - usually two poles. So did the ancient Israelites:
"The Levites carried the ark of God with poles on their shoulders, as Moses had commanded in accordance with the word of the LORD." (1 Chronicles 15:15)
The Israeli ark of the covenant had two poles (Exodus 25:10-15).
Some restored models of the ark as it was imagined to be have used two poles on the upper parts of the ark. But the Bible says those poles were to be fastened to the ark by the four rings "on its four feet" (Exodus 25:12). Hence, the poles must have been attached on the bottom of the ark. This is similar to the Japanese "omikoshi."
The Israeli ark had two statues of gold cherubim on its top. Cherubim are a type of angel, heavenly being having wings like birds. Japanese "omikoshi" also have on its top the gold bird called "Ho-oh" which is an imaginary bird and a mysterious heavenly being.
The entire Israeli ark was overlaid with gold. Japanese "omikoshi" are also overlaid partly and sometimes entirely with gold. The size of an "omikoshi" is almost the same as the Israeli ark. Japanese "omikoshi" could be a remnant of the ark of ancient
Many Things Concerning the Ark Resemble Japanese Customs.
King David and people of
Several years ago, I saw an American-made movie titled "King David" which was a faithful story of the life of King David. In the movie, David was seen dancing in front of the ark while it was being carried into
At the Shinto shrine festival of "Gion-jinja" in
In a Japanese island of the Inland Sea of Seto, the men selected as the carriers of the "omikoshi" stay together at a house for one week before they would carry the "omikoshi." This is to prevent profaning themselves. Furthermore on the day before they carry "omikoshi," the men bathe in seawater to sanctify themselves. This is similar to an ancient Israelite custom:
"So the priests and the Levites sanctified themselves to bring up the ark of the Lord God of
The Bible says that after the ark entered Jerusalem and the march was finished, "David distributed to everyone of Israel, both man and woman, to everyone a loaf of bread, a piece of meat, and a cake of raisins" (1 Chronicles 16:3). This is similar to a Japanese custom. Sweets are distributed to everyone after a Japanese festival. It was a delight during my childhood.
The Robe of Japanese Priests Resembles the Robe of Israeli Priests.
The Bible says that when David brought up the ark into
In ancient
In Ise-jingu, one of the oldest Japanese shrines, all of the priests wear white robes. And in many Japanese Shinto shrines, especially traditional ones, the people wear white robes when they carry the "omikoshi" just like the Israelites did.
Buddhist priests wear luxurious colorful robes. However, in the Japanese Shinto religion, white is regarded as the holiest color.
The Emperor of Japan, just after he finishes the ceremony of his accession to the throne, appears alone in front of the Shinto god. When he arrives there, he wears a pure white robe covering his entire body except that his feet are naked. This is similar to the action of Moses and Joshua who removed their sandals in front of God to be in bare feet (Exodus 3:5, Joshua 5:15).
Marvin Tokayer, a rabbi who lived in
"The linen robes which Japanese Shinto priests wear have the same figure as the white linen robes of the ancient priests of

Japanese Shinto priest in white robe with fringes
The Japanese Shinto priest robe has cords of 20-30 centimeters long (about 10 inches) hung from the corners of the robe. These fringes are similar to those of the ancient Israelites. Deuteronomy 22:12 says:
"make them fringes in the... corners of their garments throughout their generations."
Fringes (tassels) were a token that a person was an Israelite. In the gospels of the New Testament, it is also written that the Pharisees "make their tassels on their garments long" (Matthew 23:5). A woman who had been suffering from a hemorrhage came to Jesus (Yeshua) and touched the "tassel on His coat" (Matthew 9:20, The New Testament: A Translation in the Language of the People, translated by Charles B. Williams).
Imagined pictures of ancient Israeli clothing sometimes do not have fringes. But their robes actually had fringes. The Jewish Tallit (prayer shawl), which the Jews put on when they pray, has fringes in the corners according to tradition.
Japanese Shinto priests wear on their robe a rectangle of cloth from their shoulders to thighs. This is the same as the ephod worn by David:
"David also wore a linen ephod." (1 Chronicles 15:27)
Although the ephod of the high priest was colorful with jewels, the ordinary priests under him wore the ephods of simple white linen cloth (1 Samuel 22:18). Rabbi Tokayer states that the rectangle of cloth on the robe of Japanese Shinto priest looks very similar to the ephod of the Kohen, the Jewish priest.
The Japanese Shinto priest puts a cap on his head just like Israeli priest did (Exodus 29:40). The Japanese priest also puts a sash on his waist. So did the Israeli priest. The clothing of Japanese Shinto priests appears to be similar to the clothing used by ancient Israelites.
Waving the Sheaf of Harvest Is Also the Custom of Japan
The Jews wave a sheaf of their first fruits of grain seven weeks before Shavuot (Pentecost, Leviticus 23:10-11), They also wave a sheaf of plants at Sukkot (the Feast of Booths, Leviticus 23:40). This has been a tradition since the time of Moses. Ancient Israeli priests also waved a plant branch when he sanctifies someone. David said, "Purge me with hyssop, and I shall be clean" [Psalm 51:7(9)]. This is also a traditional Japanese custom.

Shinto priest waving for sanctification
When a Japanese priest sanctifies someone or something, he waves a tree branch. Or he waves a "harainusa," which is made of a stick and white papers and looks like a plant. Today's "harainusa" is simplified and made of white papers that are folded in a zigzag pattern like small lightning bolts, but in old days it was a plant branch or cereals.
A Japanese Christian woman acquaintance of mine used to think of this "harainusa" as merely a pagan custom. But she later went to the
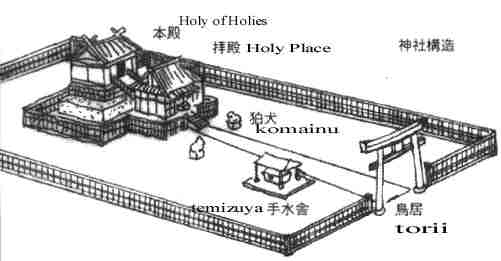
The Structure of the Japanese Shinto Shrine is Similar to God's Tabernacle of Ancient Israel
The inside of God's tabernacle in ancient
The functions performed in the Japanese shrine are similar to those of the Israeli tabernacle. Japanese pray in front of its
The Japanese Holy of Holies is located usually in far west or far north of the shrine. The Israeli Holy of Holies was located in far west of the temple. Shinto's Holy of Holies is also located on a higher level than the
Typical Japanese Shinto shrine
In front of a Japanese shrine, there are two statues of lions known as "komainu" that sit on both sides of the approach. They are not idols but guards for the shrine. This was also a custom of ancient

"Komainu" guards for shrine
In the early history of
Located near the entrance of a Japanese shrine is a "temizuya" - a place for worshipers to wash their hands and mouth. They used to wash their feet, too, in old days. This is a similar custom as is found in Jewish synagogues. The ancient tabernacle and
In front of a Japanese shrine, there is a gate called the "torii." The type gate does not exist in 
In the Israeli temple, there were two pillars used as a gate (1 Kings 7:21). And according to Joseph Eidelberg, in Aramaic language which ancient Israelites used, the word for gate was "tar'a." This word might have changed slightly and become the Japanese "torii".
Some "torii," especially of old shrines, are painted red. I can't help but think this is a picture of the two door posts and the lintel on which the blood of the lamb was put the night before the exodus from
In the Japanese Shinto religion, there is a custom to surround a holy place with a rope called the "shimenawa," which has slips of white papers inserted along the bottom edge of the rope. The "shimenawa" rope is set as the boundary. The Bible says that when Moses was given God's Ten Commandments on
The major difference between a Japanese Shinto shrine and the ancient Israeli temple is that the shrine does not have the burning altar for animal sacrifices. I used to wonder why Shinto religion does not have the custom of animal sacrifices if Shinto originated from the religion of ancient
Shinto shrine is usually built on a mountain or a hill. Almost every mountain in
Many Shinto shrines are built with the gates in the east and the Holy of Holies in the west as we see in Matsuo grand shrine (Matsuo-taisya) in
All Shinto shrines are made of wood. Many parts of the ancient Israeli temple were also made of wood. The Israelites used stones in some places, but walls, floors, ceilings and all of the insides were overlaid with wood (1 Kings 6:9, 15-18), which was cedars from Lebanon (1 Kings 5:6). In
Many Japanese Customs Resemble Those of Ancient Israel
When Japanese people pray in front of the
 Golden bell at the entrance of Shinto shrine
Golden bell at the entrance of Shinto shrine
Japanese people clap their hands two times when they pray there. This was, in ancient
Japanese people bow in front of the shrine before and after clapping their hands and praying. They also perform a bow as a polite greeting when they meet each other. To bow was also the custom of the ancient
Ordinarily, contemporary Jews do not bow. However, they bow when reciting prayers. Modern Ethiopians have the custom of bowing, probably because of the ancient Jews who immigrated to
We Japanese have the custom to use salt for sanctification. People sometimes sow salt after an offensive person leaves. When I was watching a TV drama from the times of the Samurai, a woman threw salt on the place where a man she hated left. This custom is the same as that of the ancient Israelites. After Abimelech captured an enemy city, "he sowed it with salt" (Judges 9:45). We Japanese quickly interpret this to mean to cleanse and sanctify the city.
I hear that when Jews move to a new house they sow it with salt to sanctify it and cleanse it. This is true also in
Japanese people place salt at the entrance of a funeral home. After coming back from a funeral, one has to sprinkle salt on oneself before entering his/her house. It is believed in Shinto that anyone who went to a funeral or touched a dead body had become unclean. Again, this is the same concept as was observed by the ancient Israelites.

Japanese "sumo" wrestler sowing with salt
Japanese "sumo" wrestlers sow the sumo ring with salt before they fight. European or American people wonder why they sow salt. But Rabbi Tokayer wrote that Jews quickly understand its meaning. Japanese people offer salt every time they perform a religious offering, This is the same custom used by the Israelites:
"With all your offerings you shall offer salt." (Leviticus 2:13)
Japanese people in old times had the custom of putting some salt into their baby's first bath. The ancient Israelites washed a newborn baby with water after rubbing the baby softly with salt (Ezekiel 16:4). Sanctification and cleansing with salt and/or water is a common custom among both the Japanese and the ancient Israelites.
In the Hebrew Scriptures, the words "clean" and "unclean" often appear. Europeans and Americans are not familiar with this concept, but the Japanese understand it. A central concept of Shinto is to value cleanness and to avoid uncleanness. This concept probably came from ancient
Similar to Judaism, in Japanese Shinto Religion, There Are No Idols
Buddhist temples have idols which are carved in the shape of Buddha and other gods. However in Japanese Shinto shrines, there are no idols.
In the center of the Holy of Holies of a Shinto shrine, there is a mirror, sword, or pendant. Nevertheless, Shinto believers do not regard these items as their gods. In Shinto, gods are thought to be invisible. The mirror, sword, and pendant are not idols but merely objects to show that it is a holy place where invisible gods come down.
In the ark of the covenant of ancient
Old Japanese Words Have Hebrew Origin
Joseph Eidelberg, a Jew who once came to
We say "anta" to mean "you," which is the same in Hebrew. Kings in ancient
When we Japanese count, "One, two, three... ten," we sometimes say:
"Hi, fu, mi, yo, itsu, mu, nana, ya, kokono, towo."
This is a traditional expression, but its meaning is unknown it is thought of as being Japanese.
It has been said that this expression originates from an ancient Japanese Shinto myth. In the myth, the female god, called "Amaterasu," who manages the world's sunlight, once hid herself in a heavenly cave, and the world became dark. Then, according to the oldest book of Japanese history, the priest called "Koyane" prayed with words before the cave and in front of the other gods to have "Amaterasu" come out. Although the words said in the prayer are not written, a legend says that these words were, "Hi, fu, mi...."

"Amaterasu" is hiding in a heavenly cave; "Koyane" is praying and "Uzume" is dancing.
Joseph Eidelberg stated that this is a beautiful Hebrew expression, if it is supposed that there were some pronunciation changes throughout history. These words are spelled:
"Hifa mi yotsia ma na'ne ykakhena tavo."
![]()
This means: "The beautiful (Goddess). Who will bring her out? What should we call out (in chorus) to entice her to come?" This surprisingly fits the situation of the myth.
Moreover, we Japanese not only say, "Hi, hu, mi...," but also say with the same meaning:
"Hitotsu, futatsu, mittsu, yottsu, itsutsu, muttsu, nanatsu, yattsu, kokonotsu, towo."
Here, "totsu" or "tsu" is put to each of "Hi, hu, mi..." as the last part of the words. But the last "towo" (which means ten) remains the same. "Totsu" could be the Hebrew word "tetse," which means, "She comes out. " And "tsu" may be the Hebrew word "tse" which means "Come out."
Eidelberg believed that these words were said by the gods who surrounded the priest, "Koyane." That is, when "Koyane" first says, "Hi," the surrounding gods add, "totsu" (She comes out) in reply, and secondly, when "Koyane" says, "Fu," the gods add "totsu" (tatsu), and so on. In this way, it became "Hitotsu, futatsu, mittsu...."
However, the last word, "towo," the priest, "Koyane," and the surrounding gods said together. If this is the Hebrew word "tavo," it means, "(She) shall come." When they say this, the female god, "Amaterasu," came out.
"Hi, fu, mi..." and "Hitotsu, futatsu, mittsu..." later were used as the words to count numbers.
In addition, the name of the priest, "Koyane," sounds close to a Hebrew word, "kohen," which means, "a priest." Eidelberg showed many other examples of Japanese words (several thousand) which appeared to have a Hebrew origin. This does not appear to be accidental.
In ancient Japanese folk songs, many words appear that are not understandable as Japanese. Dr. Eiji Kawamorita considered that many of them are Hebrew. A Japanese folk song in
Youtube: Similarities between Hebrew and Japanese
Similarity Between the Biblical Genealogy and Japanese Mythology
There is a remarkable similarity between the Biblical article and Japanese mythology. A Japanese scholar points out that the stories around Ninigi in the Japanese mythology greatly resemble the stories around Jacob in the Bible.
In the Japanese mythology, the Imperial family of
In the Japanese mythology, it was not Ninigi who was to come down from heaven, but the other. But when the other was preparing, Ninigi was born and in a result, instead of him, Ninigi came down from heaven and became the ancestor of the Japanese nation. In the same way, according to the Bible, it was Esau, Jacob's elder brother, who was to become God's nation but in a result, instead of Esau, God's blessing for the nation was given to Jacob, and Jacob became the ancestor of the Israelites.
And in the Japanese mythology, after Ninigi came from heaven, he fell in love with a beautiful woman named Konohana-sakuya-hime and tried to marry her. But her father asked him to marry not only her but also her elder sister. However the elder sister was ugly and Ninigi gave her back to her father. In the same way, according to the Bible, Jacob fell in love with beautiful Rachel and tried to marry her (Genesis chapter 29). But her father says to Jacob that he cannot give the younger sister before the elder, so he asked Jacob to marry the elder sister (Leah) also. However the elder sister was not so beautiful, Jacob disliked her. Thus, there is a parallelism between Ninigi and Jacob.
And in the Japanese mythology, Ninigi and his wife Konohana-sakuya-hime bear a child named Yamasachi-hiko. But Yamasachi-hiko is bullied by his elder brother and has to go to the country of a sea god. There Yamasachi-hiko gets a mystic power and troubles the elder brother by giving him famine, but later forgives his sin. In the same way, according to the Bible, Jacob and his wife Rachel bear a child named Joseph. But Joseph is bullied by his elder brothers and had to go to
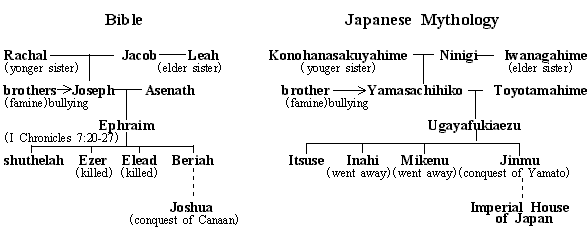
Similarity between the biblical genealogy and Japanese mythology
And in the Japanese mythology, Yamasachi-hiko married a daughter of the sea god, and bore a child named Ugaya-fukiaezu. Ugaya-fukiaezu had 4 sons. But his second and third sons were gone to other places. The forth son is emperor Jinmu who conquers the
While, what is it in the Bible? Joseph married a daughter of a priest in
Thus we find a remarkable similarity between the biblical genealogy and Japanese mythology - between Ninigi and Jacob, Yamasachi-hiko and Joseph, and the Imperial family of
Furthermore, in the Japanese mythology, the heaven is called Hara of Takama (Takama-ga-hara or Takama-no-hara). Ninigi came from there and founded the Japanese nation. Concerning this Hara of Takama, Zen'ichirou Oyabe, a Japanese researcher, thought that this is the city
Jacob once saw in a dream the angels of God ascending and descending between the heaven and the earth (Genesis 28:12), when Jacob was given a promise of God that his descendants would inherit the
Thus, except for details, the outline of the Japanese mythology greatly resembles the records of the Bible. It is possible to think that the myths of Kojiki and Nihon-shoki, the Japanese chronicles written in the 8th century, were originally based on Biblical stories but later added with various pagan elements. Even it might be possible to think that the Japanese mythology was originally a kind of genealogy which showed that the Japanese are descendants from Jacob, Joseph, and Ephraim.
Impurity during Menstruation and Bearing Child
The concept of uncleanness during menstruation and bearing child has existed in
This resembles ancient Israeli custom very much. In ancient Israel, woman during menstruation could not attend holy events at the temple, had to be apart from her husband, and it was custom to shut herself up in a hut during her menstruation and 7 days after the menstruation (Leviticus 15:19, 28). This shutting herself up was said "to continue in the blood of her purification", and this was for purification and to make impurity apart from the house or the village.

Menstruation hut used by Falasha, Ethiopian Jews
This remains true even today. There are no sexual relations, for the days of menstruation and an additional 7 days. Then the woman goes to the Mikveh, ritual bath. The water of the Mikveh must be natural water. There are cases of gathering rainwater and putting it to the Mikveh bathtub. In case of not having enough natural water, water from faucet is added.
Modern people may feel irrational about this concept but women during menstruation or bearing child need rest physically and mentally. Woman herself says that she feels impure in her blood in the period. "To continue in the blood of her purification" refers to this need of rest of her blood.
Not only concerning menstruation, but also the concept concerning bearing child in Japanese Shinto resembles the one of ancient
A mother who bore a child is regarded unclean in a certain period. This concept is weak among the Japanese today, but was very common in old days. The old Shinto book, Engishiki (the 10th century C.E.), set 7 days as a period that she cannot participate in holy events after she bore a child. This resembles an ancient custom of
In Japan it had been widely seen until Meiji era that woman during pregnancy and after bearing child shut herself up in a hut (called Ubu-goya in Japanese) and lived there. The period was usually during the pregnancy and 30 days or so after she bore a child (The longest case was nearly 100 days). This resembles the custom of ancient
In ancient
But when they come to the shrine, it is not the mother who carries the baby. It is a traditional custom that the baby should be carried not by the mother, but usually by the husband's mother (mother-in-law). This is a remarkable similarity of purity and impurity of the mother, after childbirth, with ancient Israeli custom.
Japanese "Mizura" and Jewish Peyot
The photo below (left) is a statue of an ancient Japanese Samurai found in relics of the late 5th century C.E. in


Ancient Japanese Samurai's hair style "mizura" (left) and Jewish "peyot" (right)
Is it a mere coincidence that this resembles Jewish "peyot" (payot) very much, which is also a hair style of hanging the hair in front of the ears long with some curling (photo right)? "Peyot" is a unique hair style for Jews and the origin is very old. Leviticus 19:27 of the Bible mentions:
"'Do not cut the hair at the sides of your head."
So, this custom originated from the ancient Israelites. The "peyot" custom of today's Hasidic Jews is a recovery of this ancient custom. Yemenite Jews have had this custom since ancient times. There is a statue from
DNA Shows Connection of the Japanese and Jews
Male cell has Y-chromosome, which is a hangar of DNA. Y-chromosome DNA is handed from father to son, only through the male line.
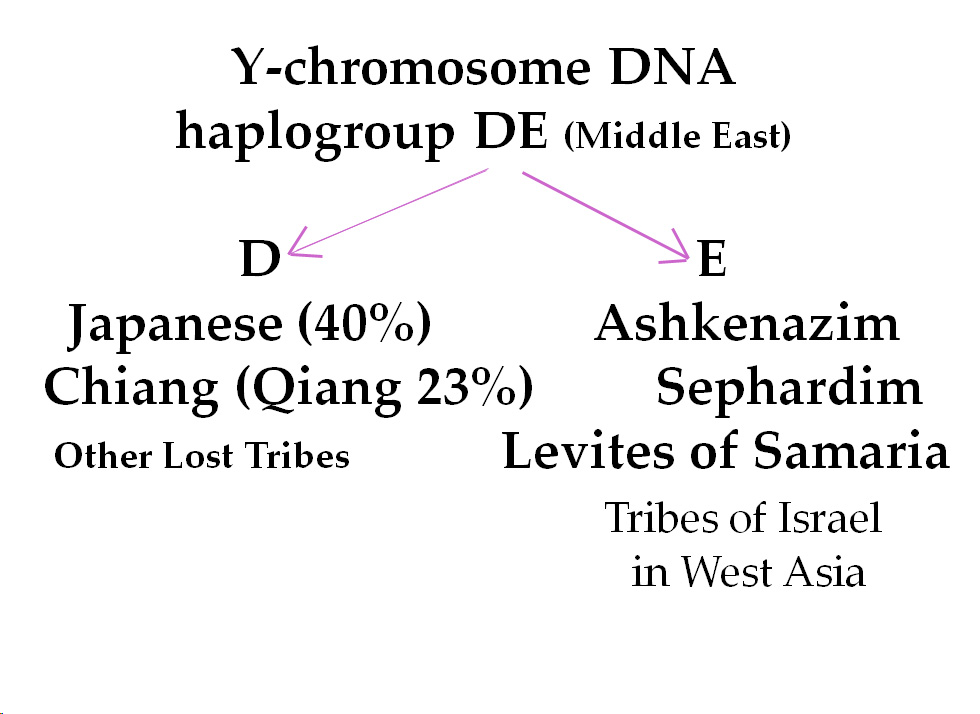
Y-chromosome DNA of Japanese males have a very specific feature which is seldom seen among the Chinese or Koreans. Nearly 40% of the Japanese have the specific gene sequence called YAP in their Y-chromosome DNA. This YAP gene sequence is seldom seen among the Chinese or Koreans, and rare in Asia. But nearly 40% of the Japanese have it.
Y-chromosome DNA has many types called haplogroups. Among all the haplogroups, only haplogroup D and haplogroup E have YAP gene sequence. Only D and E have the common YAP genes, showing they came from the same ancestor. Please memorize D and E. They are relatives. Nearly 40% of the Japanese belong to haplogroup D, having YAP gene sequence. Originally in the Middle East there was haplogroup DE, which was later separated to D and E.
Then, what is haplogroup E? It is the relative of D. Haplogroup E is very characteristic for Jews. 20-30% of both Ashkenazi Jews and Sephardi Jews have haplogroup E, which contains YAP gene sequence just like the Japanese one. Not only them, but also every other Jewish population of all over the world have haplogroup E prominently. Since D and E came from the same ancestor, they are all relatives.
This haplogroup E is also seen in Samaria, the homeland of the so-called the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel. Today in Samaria live descendants of ancient Israelites. They are of mixed blood. But according to the Bible, priests among the Samaritans are Levites, who have been keeping the male line since ancient times. The Samaritan Levite priests belong to haplogroup E, having YAP.
And in the land near Tibet in China live a small tribe called Chiang (Qiang, Chiang-Min). Their faces look like the Japanese. They are descendants of the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel, as recognized by Amishav in Jerusalem, a famous searching group of the Lost Tribes of Israel. The 23% of the Chiang people have haplogroup D, having YAP just like the Japanese do. The Chiang people and the Japanese are thus genetically relatives.
The YAP gene sequence of haplogroups D and E tells the strong connection among current Jews, descendants of ancient Israelites along the Silk Road and the Japanese.
To be continued to:
Chapter 2 - The Ten Lost Tribes of Israel in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Kashmir, Myanmar, and China
Chapter 3 - Did the Lost Tribes of Israel Come To Ancient Japan?
Chapter 4 - Various Other Similarities Between Ancient Israel and Ancient Japan
Please feel free to print this site for your personal use, and distribute it to your friends.
Remnant Publishing
E-mail: remnant@mte.biglobe.ne.jp (Your thoughts and opinions are welcome, although I may not be able to reply to all.)
Home-page is here.
For more information
Video on Israelites and the Japanese

I appeared in a Japanese TV program on this topic, broadcasted from a major TV station. The program was entitled "The Roots of Japan Were Ancient Israel!?" You can watch it at YouTube in English, Russian and Japanese.
(For English subtitles, click "Subtitles" (captions) at the right bottom of the YouTube screen)
Recommended books:
The following are the books written by Jewish researchers on the connections between the Israelites and the Japanese.
*In the Footsteps of the Lost Ten Tribes, written by Avigdor Shachan (English and Hebrew).
*The Tribes of Israel - The Lost and the Dispersed, written by Rabbi Eliyahu Avichail (English and Hebrew).
*The Biblical Hebrew Origin of the Japanese People, written by Joseph Eidelberg (English and Hebrew).
*The Japanese and the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel, written by Joseph Eidelberg
*If you can read Japanese, "Nihon-Yudaya, Huuin no Kodaishi" which is written by Rabbi Marvin Tokayer and published by Tokuma-shoten is the best book on this topic (This book includes many pictures. The English version is not published yet).
The Mystery of Jews in Japan (video)
Who are the Japanese?
Bnei Menashe
Japanese-Jewish Resources
Straight Talk About God (Lost Tribes)
Was Japanese Culture Influenced by Ancient Israel
0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿