 | Pavlina R Tcherneva (@ptcherneva) |
|
Are you scared of the the #JobGuarantee?
Have you heard that it's hostile or antithetical to welfare or unions? Let me try to help. pic.twitter.com/AjtbFD2Bai | |
Pavlina R Tcherneva Are you scared of the the #JobGuarantee? 2020/08/22
 | Pavlina R Tcherneva (@ptcherneva) |
|
10. As i always point out, the JG is being asked an impossible task - to remake the public sector and fill the many gaps of our broken and abused-by-austerity government services, and achieve many other social goals. The JG is an critical ally and precondition for many. pic.twitter.com/uNbpAzJSAL
| |
 | Pavlina R Tcherneva (@ptcherneva) |
|
11. Public institutions need to be permanently staffed, with appropriately skilled workers as needed. 12. In an ideal world JG will be small. But it is required b/c the alternative is the unemployment YoYo, with all the harms in brings. It's not an ideal world, JG could be large pic.twitter.com/KN8kwDFxOg | |
 | Pavlina R Tcherneva (@ptcherneva) |
|
13. The argument that there aren't enough useful projects for those who seek work in the JG is wrong. It betrays lack of imagination and an odd belief that some people have nothing to contribute to society. Especially bizarre when it comes from the left. pic.twitter.com/mDYsvrxCmm | |
 | Pavlina R Tcherneva (@ptcherneva) |
|
14. Low wage workers were mass casualties in the pandemic. What's their guarantee that they can get a job? What's the guarantee it will be a living-wage job? A union job, which is even harder to come by? The JG is the "stepping stone" the "bridge". pewsocialtrends.org/2020/04/21/abo… https://www.pewsocialtrends.org/2020/04/21/about-half-of-lower-income-americans-report-household-job-or-wage-loss-due-to-covid-19/
| |
About Half of Lower-Income Americans Report Household Job or Wage Loss Due to COVID-19 | Pew Research Center
https://www.pewsocialtrends.org/2020/04/21/about-half-of-lower-income-americans-report-household-job-or-wage-loss-due-to-covid-19/About Half of Lower-Income Americans Report Household Job or Wage Loss Due to COVID-19
Only 23% say they have emergency funds that would last them three months
April 21, 2020

A woman with two children waits to receive a box of food at a food bank’s mobile pickup site in Orlando, Florida, on April 6. (Paul Hennessy/NurPhoto via Getty Images)
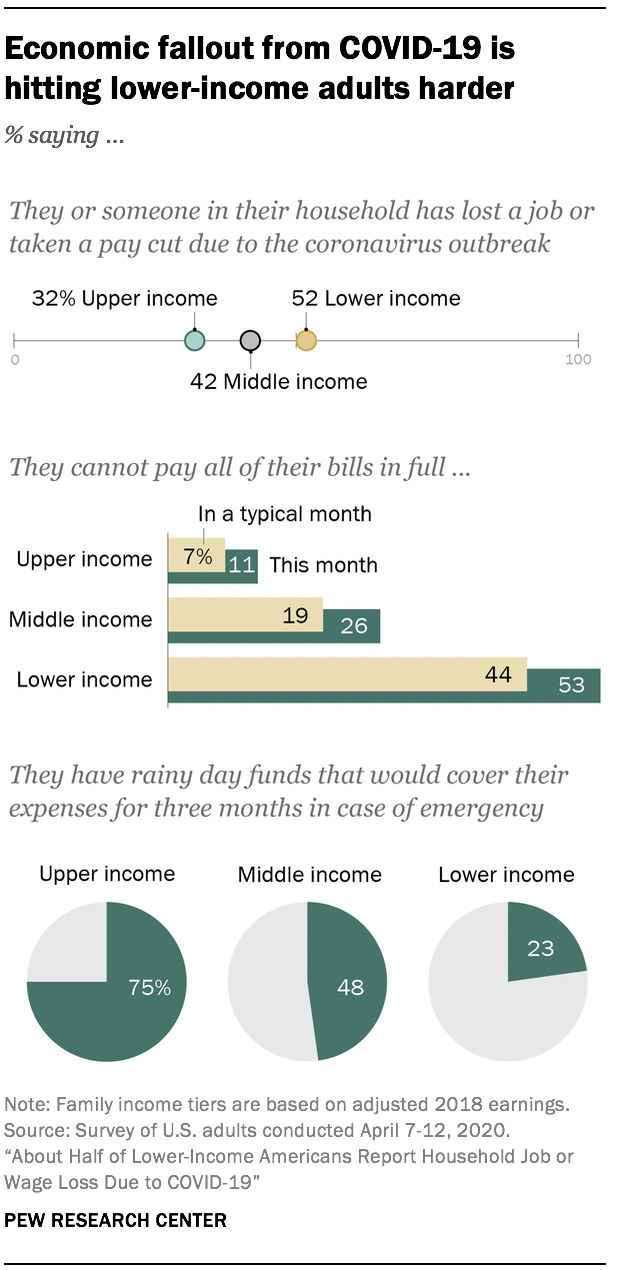 As the economic toll from the coronavirus outbreak continues to mount, a new Pew Research Center survey finds the impact is falling more heavily on lower-income adults – a group that was feeling significant financial pressure well before the current crisis. Overall, 43% of U.S. adults now say that they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay due to the outbreak, up from 33% in the latter half of March. Among lower-income adults, an even higher share (52%) say they or someone in their household has experienced this type of job upheaval.
As the economic toll from the coronavirus outbreak continues to mount, a new Pew Research Center survey finds the impact is falling more heavily on lower-income adults – a group that was feeling significant financial pressure well before the current crisis. Overall, 43% of U.S. adults now say that they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay due to the outbreak, up from 33% in the latter half of March. Among lower-income adults, an even higher share (52%) say they or someone in their household has experienced this type of job upheaval.
In addition to being among the hardest hit by the economic fallout from COVID-19, lower-income adults are less prepared to withstand a financial shock than those with higher incomes. Only about one-in-four (23%) say they have rainy day funds set aside that would cover their expenses for three months in case of an emergency such as job loss, sickness or an economic downturn, compared with 48% of middle-income and 75% of upper-income adults.1 And while 53% of lower-income adults say they will have trouble paying some of their bills this month, about a quarter of middle-income adults and 11% of those in the upper income tier say the same.
These personal experiences bring into sharp relief the public’s overall assessment of the U.S. economy. Only 23% of adults now rate national economic conditions as excellent or good, down dramatically from 57% at the beginning of 2020.
Job losses continue to be felt more acutely by some groups than others. Roughly six-in-ten Hispanic adults (61%) say they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay due to the coronavirus outbreak. This compares with roughly half or fewer of black and white adults. And adults without a bachelor’s degree remain more likely to report job or wage loss in their household compared with college graduates.
The extent to which U.S. adults are prepared for a financial emergency also varies significantly across demographic groups. Overall, 47% of Americans say they have rainy day funds on hand that would cover their expenses for up to three months. While this is the case for a majority of white adults, those ages 65 and older and college graduates, it’s not the norm for most other groups. For example, only about a third or fewer of black and Hispanic adults, those younger than 30 and those with no college experience say they have this type of rainy day fund.
Among those who don’t have emergency funds, relatively few say they could tap into other resources in order to make ends meet. Only 28% say they would be able to cover their basic expenses by borrowing money, using their savings or selling assets.
Even without a financial emergency, many Americans say they have trouble paying their monthly bills. About one-in-four adults (24%) say they cannot pay some of their bills or can only make partial payment on them in a typical month. A larger share (32%) say they won’t be able to pay their bills this month. The gap in the share saying they won’t be able to pay their bills this month compared with an average month is particularly wide among Hispanic adults: 44% say they won’t be able to pay all of their bills this month, while 28% say this is typically the case.
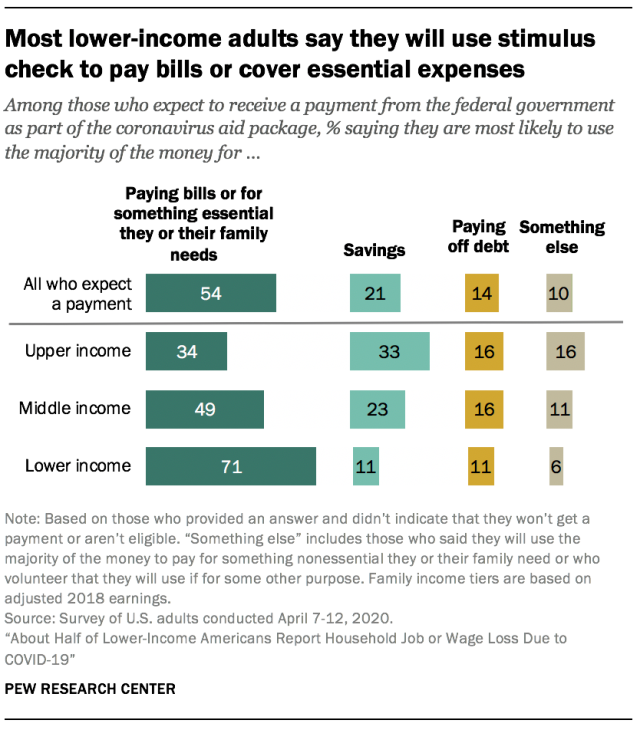 Given these financial constraints, more than half of adults who expect to receive a direct payment from the federal government as part of its coronavirus aid package say they will use a majority of the money to pay bills or for something essential for themselves or their family. About one-in-five (21%) say they will save a majority of the money, and 14% say they will use it to pay off debt. The remaining 10% say they’ll use it for something else.2 Again, there are differences by key demographic groups, with black and Hispanic adults, those without a college degree and those in the lower-income tier more likely to say they will use the money to pay bills or cover essential needs.
Given these financial constraints, more than half of adults who expect to receive a direct payment from the federal government as part of its coronavirus aid package say they will use a majority of the money to pay bills or for something essential for themselves or their family. About one-in-five (21%) say they will save a majority of the money, and 14% say they will use it to pay off debt. The remaining 10% say they’ll use it for something else.2 Again, there are differences by key demographic groups, with black and Hispanic adults, those without a college degree and those in the lower-income tier more likely to say they will use the money to pay bills or cover essential needs.
These are among the findings of a Pew Research Center survey of 4,917 U.S. adults conducted April 7-12, 2020, using the Center’s American Trends Panel.3
Public reports widespread job disruption amid coronavirus outbreak
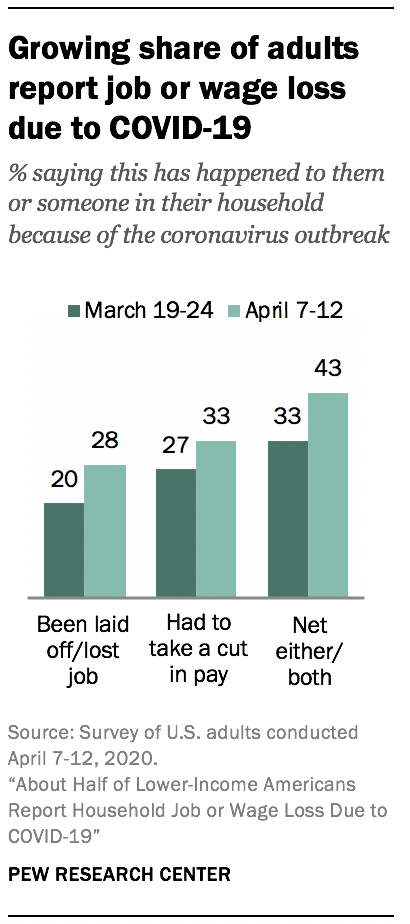 Amid mounting unemployment claims, the share of American households that have experienced job loss or disruption has climbed significantly in recent weeks. Roughly three-in-ten adults (28%) say they or someone in their household has been laid off or lost their job because of the coronavirus outbreak. A third say they or someone in their household has had to take a cut in pay due to reduced hours or demand for their work. Taken together, 43% of adults say they have experienced at least one or both of these.
Amid mounting unemployment claims, the share of American households that have experienced job loss or disruption has climbed significantly in recent weeks. Roughly three-in-ten adults (28%) say they or someone in their household has been laid off or lost their job because of the coronavirus outbreak. A third say they or someone in their household has had to take a cut in pay due to reduced hours or demand for their work. Taken together, 43% of adults say they have experienced at least one or both of these.
These shares are up significantly from just three weeks earlier. At that time, 20% of adults reported job loss, 27% reported pay reduction and 33% said they or someone in their household had experienced either or both.
As was the case last month, these experiences are more concentrated among certain demographic groups. Hispanic adults are more likely than white or black adults to say they or someone in their household has experienced job or wage loss because of the coronavirus outbreak. Roughly six-in-ten Hispanics (61%) say this has happened in their household, compared with 44% of black adults and 38% of whites.
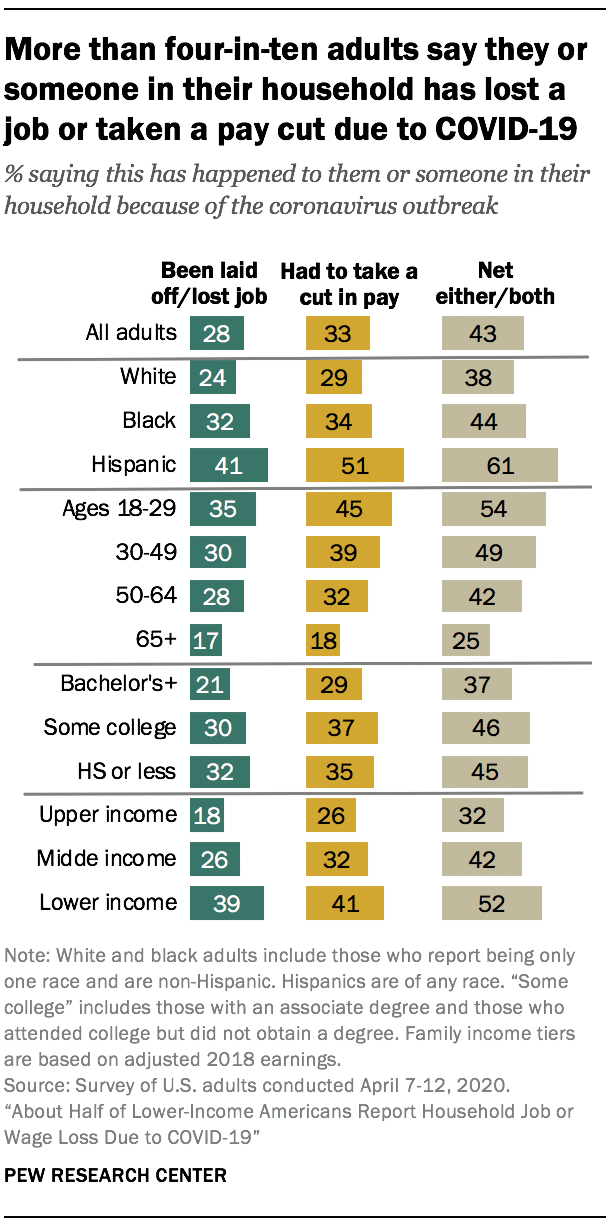 Lower-income adults are more likely than middle- and upper-income adults to say they’ve experienced significant job disruption due to the coronavirus outbreak. About half of lower-income adults (52%) say they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay due to the outbreak. This compares with 42% of middle-income and 32% of upper-income adults.
Lower-income adults are more likely than middle- and upper-income adults to say they’ve experienced significant job disruption due to the coronavirus outbreak. About half of lower-income adults (52%) say they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay due to the outbreak. This compares with 42% of middle-income and 32% of upper-income adults.
These experiences also differ by educational attainment, with college graduates more insulated from the impact of the coronavirus outbreak. While 46% of those without a bachelor’s degree say they or someone in their household has lost a job or taken a cut in pay, smaller shares of bachelor’s degree holders (37%) say the same.
Though some demographic groups have been more hard hit than others, increases in the share of Americans experiencing job upheaval in recent weeks are widespread. Across racial and ethnic groups, income tiers, and educational backgrounds, the share of adults saying their household has experienced job or wage loss due to the coronavirus outbreak has gone up in recent weeks. The gaps across age groups that were apparent in March are less pronounced now, as adults ages 30 to 49 are now as likely as those younger than 30 to say they’ve experienced a major job setback.
Many adults have rainy day funds, but shares differ widely by race, education and income
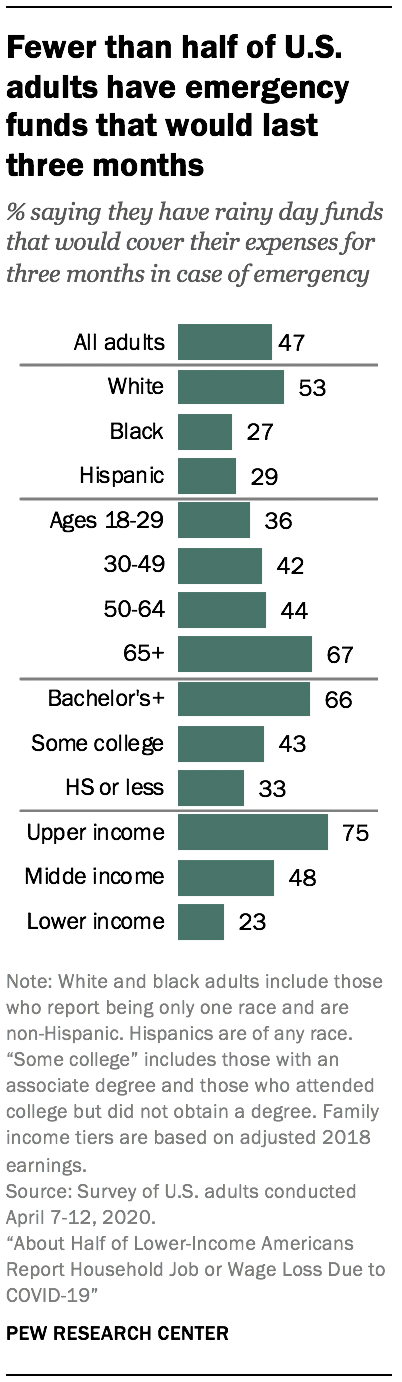 For Americans who have suffered job loss or seen their paychecks diminished, cash reserves can be a temporary lifeline. Fewer than half of all adults (47%) say they have emergency or rainy day funds that would cover their expenses for three months in case of sickness, job loss, economic downturn, or other emergencies; 53% say they don’t have this type of savings on hand.
For Americans who have suffered job loss or seen their paychecks diminished, cash reserves can be a temporary lifeline. Fewer than half of all adults (47%) say they have emergency or rainy day funds that would cover their expenses for three months in case of sickness, job loss, economic downturn, or other emergencies; 53% say they don’t have this type of savings on hand.
The share who have rainy day funds differs drastically across demographic groups, and the groups that have been hardest hit by job and wage losses during the COVID-19 crisis are among the least likely to have these types of reserves. While 53% of white adults say they have rainy day funds, much smaller shares of Hispanic (29%) and black adults (27%) say the same.
Upper-income adults are roughly three times as likely as lower-income adults to say they have emergency funds that would cover their expenses for three months – 75% vs. 23%. Among middle-income adults, 48% say they have such funds.
Similarly, about two-thirds of adults with a bachelor’s degree or more education (66%) say they have rainy day funds that would carry them through for three months. The shares are significantly lower for those with some college education (43%) or a high school degree or less (33%).
A majority of adults ages 65 and older (67%) say they have emergency funds set aside. By contrast, fewer than half of those younger than 65 say the same. Even among those ages 50 to 64, the share is only 44%.
Among adults who say they or someone in their household have lost a job or taken a pay cut due to the coronavirus outbreak, most don’t have emergency funds to fall back on. Only 38% say they have rainy day funds that would cover their expense for three months.
Most adults who don’t have emergency funds would have a hard time accessing funds to cover basic expenses if they lost their income
Of the 53% of adults who say they don’t have rainy day funds set aside, most say they wouldn’t have easy access to money that could help them meet their financial obligations if they lost their main source of income. Only 28% say they would be able to cover their expenses for three months by borrowing money, using savings, selling assets, or borrowing from friends or family. About seven-in-ten (71%) say they would not be able to do this.
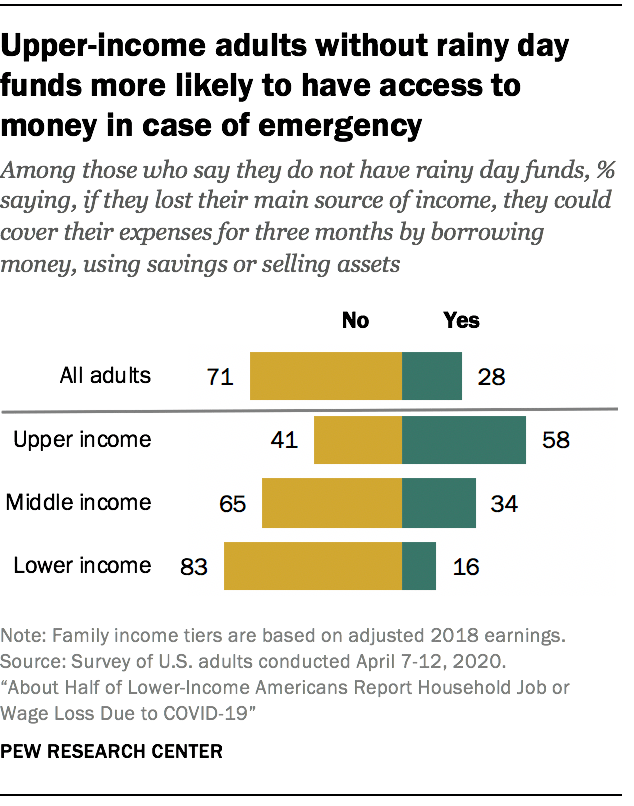 Among those without emergency funds, white adults, upper-income adults and those with a bachelor’s degree or more education are among the most likely to say they’d be able to cover their expenses by borrowing money, relying on savings or liquidating assets. For example, while 58% of upper-income adults who don’t have rainy day funds say they could cover their expenses for three months by tapping into other resources, only 34% of middle-income adults and 16% of lower-income adults without emergency funds say they could do the same.
Among those without emergency funds, white adults, upper-income adults and those with a bachelor’s degree or more education are among the most likely to say they’d be able to cover their expenses by borrowing money, relying on savings or liquidating assets. For example, while 58% of upper-income adults who don’t have rainy day funds say they could cover their expenses for three months by tapping into other resources, only 34% of middle-income adults and 16% of lower-income adults without emergency funds say they could do the same.
Although older adults are more likely than middle-aged and younger adults to have rainy day funds, among those who don’t, older adults are just as likely as their younger counterparts to say they wouldn’t be able to cover their expenses by borrowing money or using their own savings.
More say they won’t be able to pay some of their bills this month than say they can’t do this in a typical month
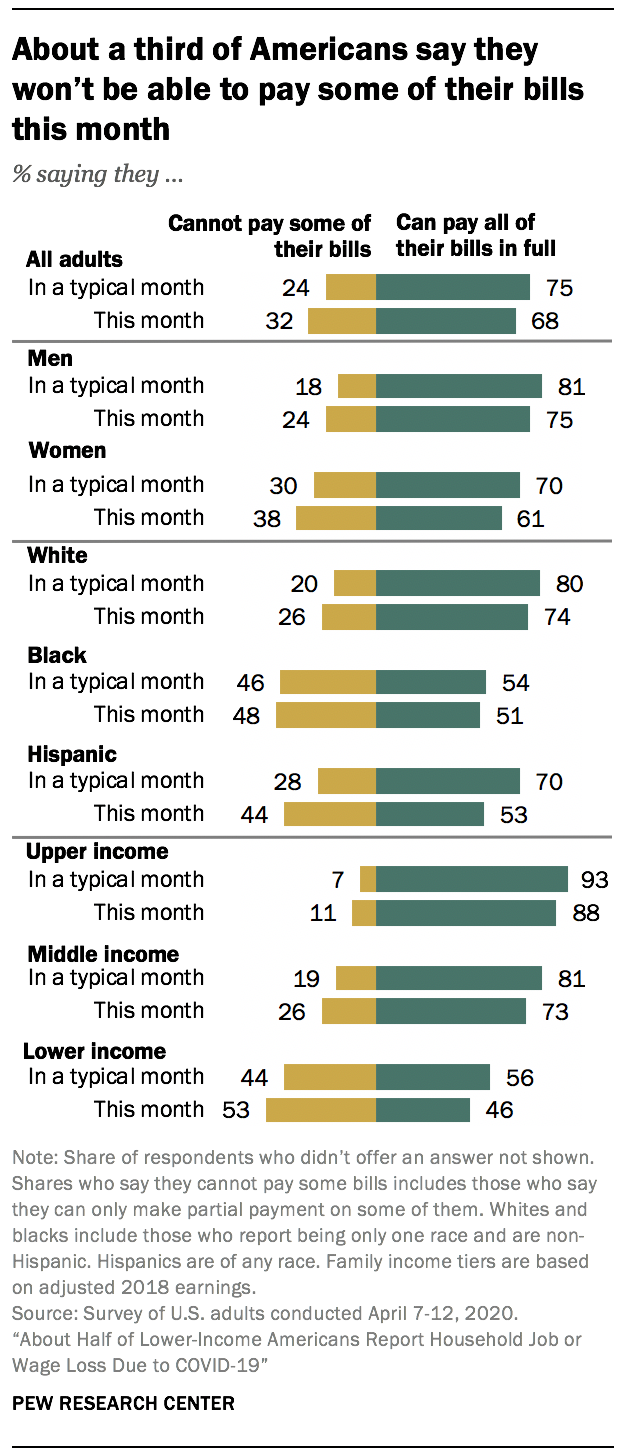 Three-quarters of Americans say they can typically pay all of their bills in full, while 24% say that, in a typical month, they cannot pay some bills or can only make partial payment on some of them. When asked about their ability to pay their bills this month, a larger share (32%) say they won’t be able to pay some bills than say this is the case in a typical month.
Three-quarters of Americans say they can typically pay all of their bills in full, while 24% say that, in a typical month, they cannot pay some bills or can only make partial payment on some of them. When asked about their ability to pay their bills this month, a larger share (32%) say they won’t be able to pay some bills than say this is the case in a typical month.
Women are more likely than men to say they cannot pay some bills – either in a typical month or this month in particular. The share of women who say they will not be able to pay some bills this month is larger than the share who say this is the case in a typical month (38% vs. 30%).
There are also differences across racial and ethnic groups, with black adults particularly likely to say they cannot pay some bills or can only make partial payment on some of them in a typical month: 46% of black adults say this, compared with 28% of Hispanic adults and an even smaller share of white adults (20%).
The share of Hispanic adults who say they will not be able to pay some bills this month (44%) is 16 percentage points higher than the share who say they cannot pay some bills in a typical month. The gap between those who say they won’t be able to pay some bills this month and those who say they aren’t able to do so in a typical month is less pronounced among white adults and not significant among black adults. Hispanics have been particularly hard hit by job losses and pay cuts related to the coronavirus outbreak.
Not surprisingly, lower-income adults are more likely than those in the middle- and upper-income tiers to say they can’t pay some bills or can only make a partial payment on some of them, both in a typical month and this month in particular. About 44% of adults with lower incomes say this is the case in a typical month, compared with 19% of those with middle incomes and just 7% of those with upper incomes. When asked about their ability to pay their bills this month, about half of those with lower incomes (53%) say they will not be able to pay some bills, while 26% of middle-income and 11% of upper-income adults say the same.
About one-in-five lower-income and black adults say the coronavirus outbreak has hurt their own personal finances more than those of most people
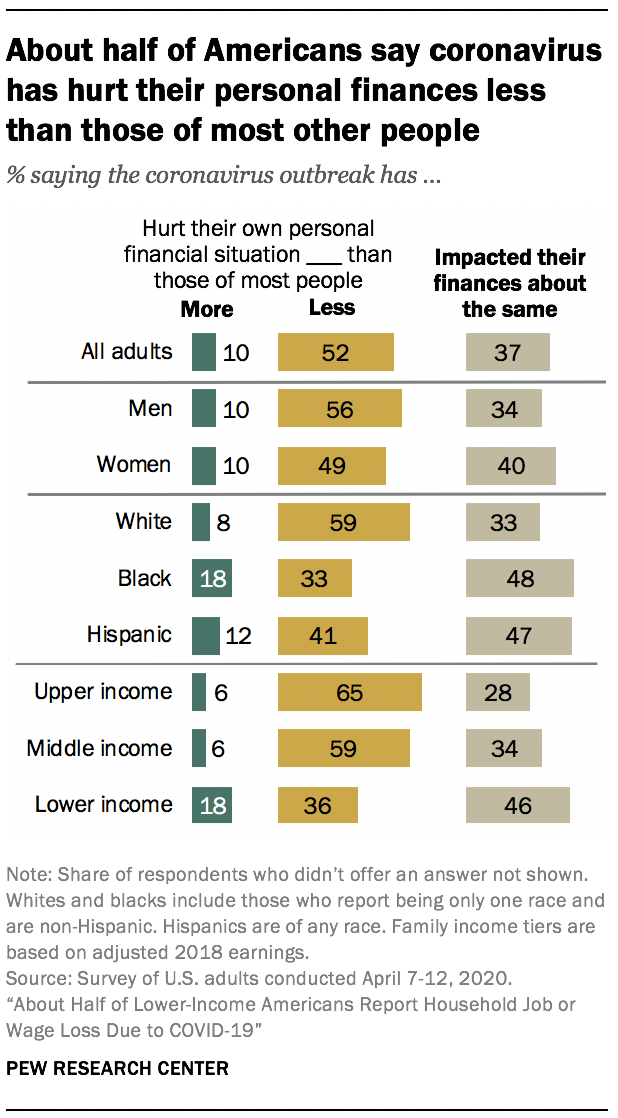 When asked for their impression of how the coronavirus outbreak has impacted their own personal financial situation compared with most other people, about half of U.S. adults (52%) say it has hurt their finances less than those of other people, while 10% say it has hurt their finances more and 37% say it has impacted their finances the same as it has most other people.
When asked for their impression of how the coronavirus outbreak has impacted their own personal financial situation compared with most other people, about half of U.S. adults (52%) say it has hurt their finances less than those of other people, while 10% say it has hurt their finances more and 37% say it has impacted their finances the same as it has most other people.
Black and lower-income adults are particularly likely to say their finances have been hurt more than those of most other people. About one-in-five black adults (18%) say this, compared with 8% of white and 12% of Hispanic adults.
Among lower-income adults, 18% say the outbreak has hurt their finances more than those of most people; just 6% of middle- and upper-income adults say the same. A majority of adults in the upper (65%) and middle (59%) income tiers say the outbreak has hurt their personal finances less than those of other people.
People who say they or someone in their household have either been laid off or taken a pay cut as a result of the coronavirus outbreak are more likely than those who haven’t had these experiences to say the outbreak has hurt their finances more than those of most other people (18% vs. 4%). Still, about four-in-ten of those who say they or someone in their household have had these experiences say their finances have been hurt less (39%) or have been impacted about the same (43%) as others.
More than half of Americans who expect to receive a payment from the government as part of the coronavirus aid package say they will use the majority of it to pay bills
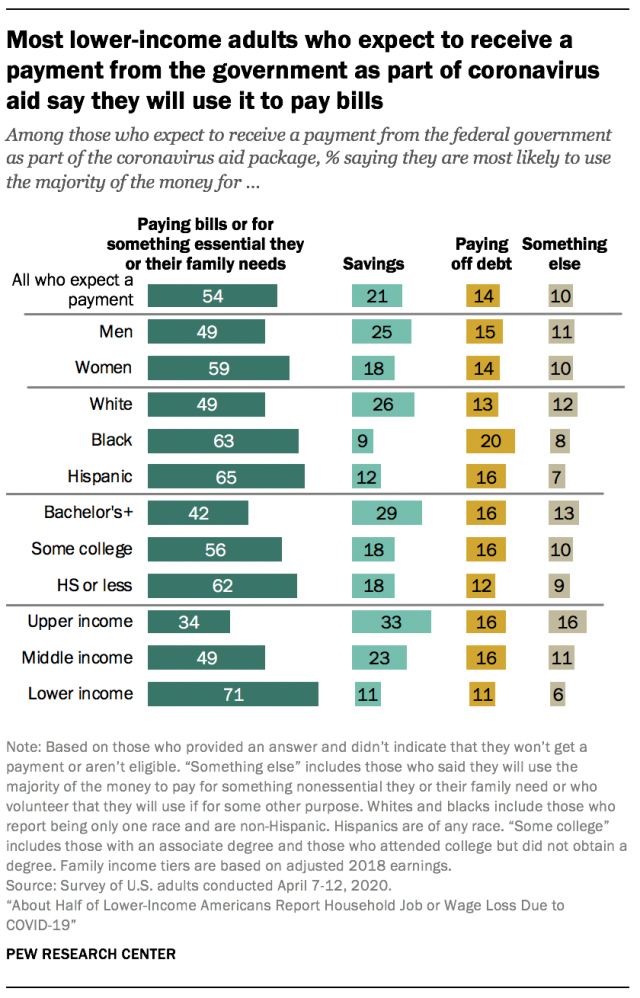 As part of a wide-reaching economic relief package, millions of Americans are receiving one-time payments from the federal government aimed at easing any financial burdens brought on by the coronavirus outbreak. Some 54% of U.S. adults who expect to receive a payment from the federal government say they are most likely to use the majority of the money to pay bills or for something essential they or their family needs; 21% say they will save the money, while 14% say they’ll pay off debt. An additional 10% say they’ll use the money for something else, including paying for something nonessential, donating to charity, helping friends and family, or some combination.
As part of a wide-reaching economic relief package, millions of Americans are receiving one-time payments from the federal government aimed at easing any financial burdens brought on by the coronavirus outbreak. Some 54% of U.S. adults who expect to receive a payment from the federal government say they are most likely to use the majority of the money to pay bills or for something essential they or their family needs; 21% say they will save the money, while 14% say they’ll pay off debt. An additional 10% say they’ll use the money for something else, including paying for something nonessential, donating to charity, helping friends and family, or some combination.
Lower-income adults who expect to receive a payment are the most likely to say they will use a majority of the money they receive to pay bills or for something essential: 71% say this, compared with 49% of middle-income adults and 34% of those with upper incomes. Among those in the upper income tier who expect to receive a payment, a third say they are likely to save a majority of it; about a quarter of middle-income adults (23%) and just 11% of those with lower incomes say the same.
There are also differences by race and ethnicity and by educational attainment. Larger shares of black and Hispanic adults than white adults say they will likely use a majority of the aid money they receive to pay bills or for something essential. Similarly, those without a bachelor’s degree are more likely than college graduates to say they will use a majority of the money for this. These racial differences are related, at least in part, to the fact that black and Hispanic adults are more likely than white adults to be in the lower-income tier. Across educational attainment, those with some college or less education remain more likely than those with at least a bachelor’s degree to say they will use the majority of the money to pay bills, even after accounting for income differences between these groups.
Overall, fewer than half of U.S. adults (46%) say the federal government’s aid package will do a great deal or a fair amount to help them and their household. By comparison, about two-thirds or more say this will help large businesses (77%), small businesses (71%), unemployed people (68%), and state and local governments (67%) at least a fair amount, and 49% say this will help people who are self-employed. Lower-income adults (59%) are more likely than those with middle (48%) or upper (22%) incomes to say the aid package will help them and their household a great deal or a fair amount.
About four-in-ten Americans frequently worry about paying their bills or saving for retirement – but these are not new concerns
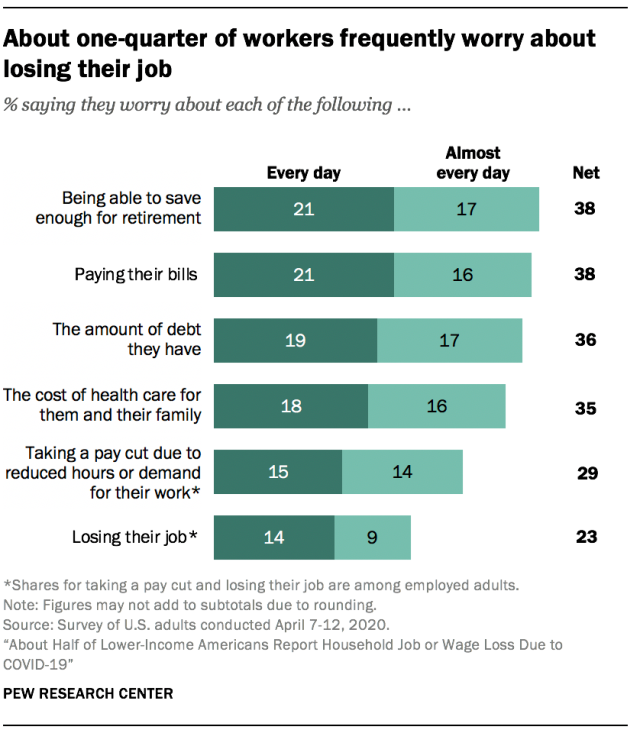 More than three-in-ten Americans say they worry every day or almost every day about being able to save enough money for their retirement (38%), paying their bills (38%), the amount of debt they have (36%), and the cost of health care for themselves and their family (35%). Smaller but substantial shares say they are worried they may have to take a pay cut due to reduced hours or demand for their work or that they will lose their job (29% and 23% of employed adults, respectively).
More than three-in-ten Americans say they worry every day or almost every day about being able to save enough money for their retirement (38%), paying their bills (38%), the amount of debt they have (36%), and the cost of health care for themselves and their family (35%). Smaller but substantial shares say they are worried they may have to take a pay cut due to reduced hours or demand for their work or that they will lose their job (29% and 23% of employed adults, respectively).
These worries may not necessarily be connected to the coronavirus outbreak. U.S. adults actually show less concern now about the amount of debt they have, their health care costs, paying their bills and being able to save enough for retirement than they did when asked some of the same questions in a September 2019 survey, well before the start of the pandemic. Similar shares of Americans who were employed at the time of each of the surveys said they regularly worried about losing their job. (The item on taking a pay cut was not asked in September.)
About half or more of lower-income adults often worry about meeting basic financial needs
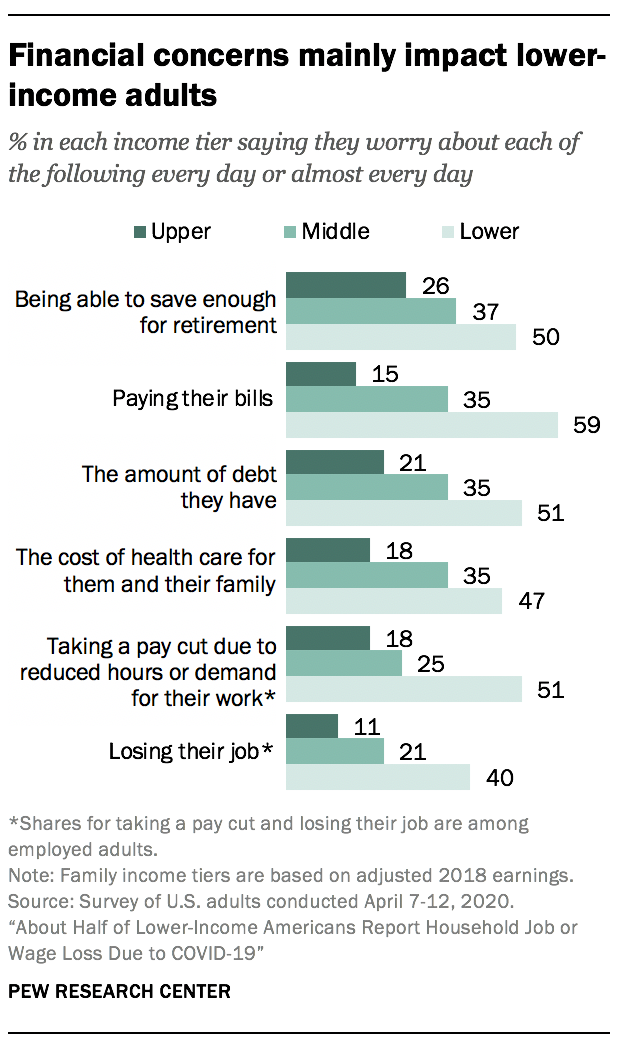 Financial concerns are not felt equally by all Americans. Those in lower-income families are at least about twice as likely as those in upper-income families to say they regularly worry about making ends meet in various ways. For example, 59% of lower-income adults say they worry at least almost every day about paying their bills, compared with 15% of upper-income adults. About half of those in the lower-income tier also say they frequently worry about saving for retirement, debt or health care costs, while about a quarter or less of their upper-income counterparts say the same.
Financial concerns are not felt equally by all Americans. Those in lower-income families are at least about twice as likely as those in upper-income families to say they regularly worry about making ends meet in various ways. For example, 59% of lower-income adults say they worry at least almost every day about paying their bills, compared with 15% of upper-income adults. About half of those in the lower-income tier also say they frequently worry about saving for retirement, debt or health care costs, while about a quarter or less of their upper-income counterparts say the same.
Across income groups, those who have been laid off or have taken a pay cut as a result of the coronavirus outbreak – or who say someone in their household has – are more likely than those who have not experienced this to say they worry about these financial concerns almost every day or more often. Roughly half (51%) of those who’ve had this type of job disruption in their household say they worry about paying their bills at least almost every day, compared with 28% of those whose household hasn’t had these experiences.
Women, black and Hispanic adults, those younger than 65, and those without bachelor’s degrees are the most likely to report regularly worrying about most of these financial issues.
- Family incomes are based on 2018 earnings and adjusted for differences in purchasing power by geographic region and for household sizes. Middle income is defined here as two-thirds to double the median annual family income for all panelists on the American Trends Panel. Lower income falls below that range; upper income falls above it.
- “Something else” includes 4% who said they will use the majority of the money to pay for something nonessential they or their family need and 7% who volunteer that they will donate it to charity, use it to help friends or family members, use it to pay their taxes, or use it for a combination of needs. These subtotals do not add up to 10% due to rounding.
- For more details, see the methodology section of the report.

Pavlina R Tcherneva 2020/08/22 #JobGuaranteeが怖いですか?
返信削除Pavlina R Tcherneva(@ptcherneva)
2020/08/22 23:43
#JobGuarantee が怖い ですか?
それが福祉や労働組合に対して敵対的であるか、または反対であると聞いたことがありますか?お手伝いさせてください。 pic.twitter.com/AjtbFD2Bai
https://twitter.com/ptcherneva/status/1297182659307802625?s=21
1. JGは、福祉用セーフティネットの欠落した部分であり、アドオンであり、代替品ではありません。我々
「雇用オプション」を追加して福祉システムを強化する。私はそれについての本全体を持っています:
2.退職所得がない場合、保証します(SocSec)
子供が教育にアクセスする必要がある場合、私たちはそれを保証します(パブ教育)
誰かが仕事を望んでいる場合、トレーニングとUIだけでは不十分です。基本的な仕事ができることを保証する必要があります。
(他の保証も必要です:住宅、m4a)
3. JG労働者は組合を結成できる。
JGの賃金は事実上の最低賃金です。デジュール最低賃金の引き上げは遅れています。両方のポリシーが連携して機能します。法定賃金の下限(最低賃金法)とそのような仕事の保証(JG)です。どちらも生産性の点で⤴️にリンクする必要があります。
4. JGが(単なる雇用プログラムではなく)構造改革であることを認めている人はほとんどいないようです。それは安定化政策の革新です。
5.それはマクロ安定装置であり、経済のすべての仕事のための妥協のない賃金フロアです。代替は何ですか?それがなければ、「失業者の予備軍」が保証される。
thisこれはJG批評家にとって好ましいオプションですか?
6.労働組合は現在の大量失業体制下でどのように公正ですか?良くない。経済がより安定し、不振の脅威が大幅に取り除かれ、基本的な賃金/福利厚生フロアが確立された場合、彼らの仕事はどのように変化しますか?私たちが失業中の回復を禁止した場合、彼らは悪化するでしょうか?いいえ
7.多くの労働者は組合化されていません。誰が代弁しますか?特に、最悪の労働市場の状況に苦しんでいるマージンの人々のために。彼らはどのようなレバレッジを持っていますか?基本的な求人がいつでも受けられると知っていたらどうでしょうか。
8.可能な限り労働者の労働組合化を目指すことができますが、それでも失業問題は解決しません。組合とJGは相互に排他的ではありません。それらは補完的です。
9.フロアとパブリックオプションは、交渉力を損なうものではなく、強化するものです。JGは、事実上の賃金/福利厚生フロアと雇用オプションを提供します。
Pavlina R Tcherneva(@ptcherneva)
2020/08/22 23:43
10.私がいつも指摘しているように、JGは不可能な仕事を求められています。公共部門を作り直し、私たちの壊れた、そして緊縮虐待政府サービスの多くのギャップを埋め、他の多くの社会的目標を達成することです。JGは多くの人にとって重要な同盟国であり、前提条件です。 pic.twitter.com/uNbpAzJSAL
Pavlina R Tcherneva(@ptcherneva)
2020/08/22 23:43
11.公的機関には、必要に応じて適切なスキルを持つ労働者を配置し、常駐させる必要があります。
12.理想的な世界では、JGは小さくなります。ただし、代替手段としては、すべての害を伴う失業率のYoYoが必要です。それは理想的な世界ではありません、JGは大きくなる可能性があります pic.twitter.com/KN8kwDFxOg
Pavlina R Tcherneva(@ptcherneva)
2020/08/22 23:43
13. JGで仕事を求める人々にとって、十分な有用なプロジェクトがないという主張は間違っています。それは想像力の欠如と社会に貢献するものを何も持っていないという奇妙な信念を裏切るものです。特に左から見ると奇妙です。 pic.twitter.com/mDYsvrxCmm
Pavlina R Tcherneva(@ptcherneva)
2020/08/22 23:43
14.低賃金労働者はパンデミックで大量死傷者でした。彼らが就職できるという彼らの保証は何ですか?それが生活賃金の仕事になる保証は何ですか?労働組合の仕事、それを手に入れるのはさらに難しいですか?
JGは「飛び石」、「橋」です。 pewsocialtrends.org/2020/04/21/abo…
15.結論としては、JGはどちらか一方のポリシーではありません。しかし、その望ましさについての議論は、1つの基準をクリアする必要があります。答えは明らかに「いいえ」です。
15.結論としては、JGはどちらか一方のポリシーではありません。しかし、その望ましさについての議論は、1つの基準をクリアする必要があります。答えは明らかに「いいえ」です。
16.他にも人々の心配や恐れがあります。それは労働者を怠惰にし、生産性を台無しにし、「大規模で非効率的な政府」につながりますか。私はこれらともっとここで答えます:
…
結局、あなたは何をもっと恐れますか?失業とその壊滅的な影響を許容し、正常化する世界、または基本的な生活賃金の仕事のオプションを確保した世界。終わり/